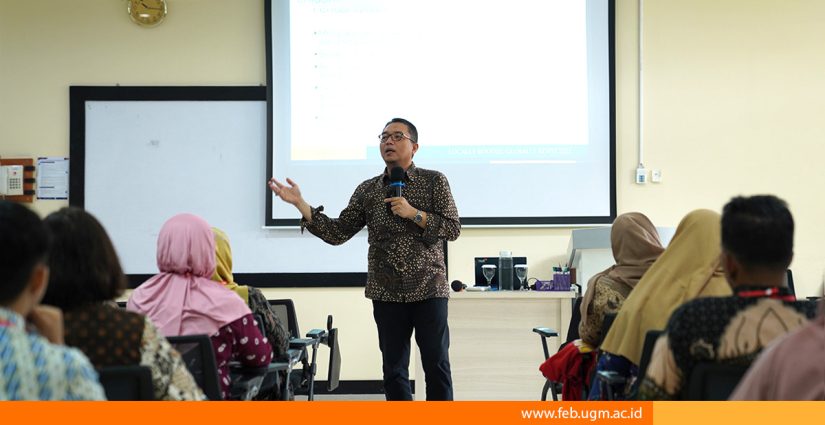
The Regional Revenue and Expenditure Budget (APBD) is a vital element in the local government system that needs to be understood by various segments of society, including teachers. As educators and key sources of information for students, teachers’ understanding of the APBD can serve as an essential bridge in broadening the younger generation’s knowledge about public financial management. During the “2025 High School Economics Teacher Training for the Yogyakarta Special Region (DIY)” held at the West Building of the Faculty of Economics and Business (FEB), Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) on Thursday (May 22, 2025), Amirullah Setya Hardi, S.E., Cand.Oecon., Ph.D., a lecturer in the Economics Department at FEB UGM and expert team member for the 2025–2029 RPJMD of Gunungkidul Regency, delivered a presentation on the APBD.
Amirullah explained that the APBD is an annual financial plan prepared by the local government and approved by the Regional Legislative Council (DPRD) to be implemented over a calendar year. The APBD is the foundation for executing various local policies to finance government activities, development programs, and public services. Its preparation does not happen instantly, instead, it begins early in the previous year and must go through a series of stages, including planning, budgeting, implementation, monitoring and evaluation, and accountability. This process is conducted in a tiered and continuous manner in line with the National Budget (APBN), beginning with the elected president’s vision and mission, which are outlined in the National Long-Term Development Plan (RPJP Nasional), then translated to the provincial and regional levels. The elected regional head’s vision and mission become the basis for formulating work programs, which are ultimately expressed through the APBD.
In practice, the preparation of the APBD is guided by several key principles, such as transparency, efficiency, effectiveness, accountability, and fairness. Its formulation also involves various aspects, including technocratic, political, economic, and socio-cultural considerations.
The APBD consists of three main components. On the revenue side, it includes Regional Original Revenue (PAD), transfer revenues, and other legitimate local revenues. Expenditures are categorized into operational spending, capital expenditure, indirect spending, and transfer expenditure. Meanwhile, regional financing covers both financing receipts and expenditures.
The funds allocated through the APBD are then used to support a wide range of local government activities, including economic development, enhancement of public services, equitable welfare distribution, and fostering regional economic growth. However, Amirullah also highlighted some challenges in this process, such as budgetary slack, which results in revenue projections being set too low and expenditure projections too high, undermining budget effectiveness.
Lastly, Amirullah emphasized that the APBD plays a crucial role in supporting sustainable regional development focused on improving public welfare. Therefore, understanding the APBD is essential for local governments and the broader public, including teachers and high school students.
Reportage: Najwah Ariella Puteri
Editor: Kurnia Ekaptiningrum
Sustainable Development Goals